News
VIETNAM’S FERTILIZER INDUSTRY ENTERS A STABLE PERIOD
Vietnam’s fertilizer industry is experiencing a period of stability and balance after a strong development chain. According to a report by the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development, the domestic fertilizer market is saturated with supply exceeding demand in the Urea/Phosphate and NPK segments. Vietnamese enterprises have been looking for ways to boost exports to other countries when global demand is high.
OVERVIEW OF VIETNAM FERTILIZER MARKET
Positive growth of fertilizer industry in 2024
Vietnam’s fertilizer production output in 2024 shows signs of positive growth. Specifically, production output increased by 16.1% compared to the same period in 2023 and increased by 0.7% compared to the same period in 2022. However, output is showing signs of slowing down since June, as the peak fertilizer consumption season has passed.
Output growth thanks to rising rice prices
In the first months of 2024, urea fertilizer output increased by 6.5% compared to the same period last year, while NPK fertilizer output increased by 11.7%. The main reason for this growth is that Vietnam’s rice export prices remain high, creating a large demand for fertilizer. Since the beginning of the year, Vietnam’s rice export prices have reached VND16,000/kg at times, significantly higher than the VND14,000/kg of the previous year.

This increase is partly due to the fact that countries such as the Philippines, Malaysia and Indonesia are facing food shortages due to natural disasters and production restrictions. This has created a great opportunity for Vietnam to boost rice exports, thereby increasing domestic fertilizer demand to meet rice production requirements.
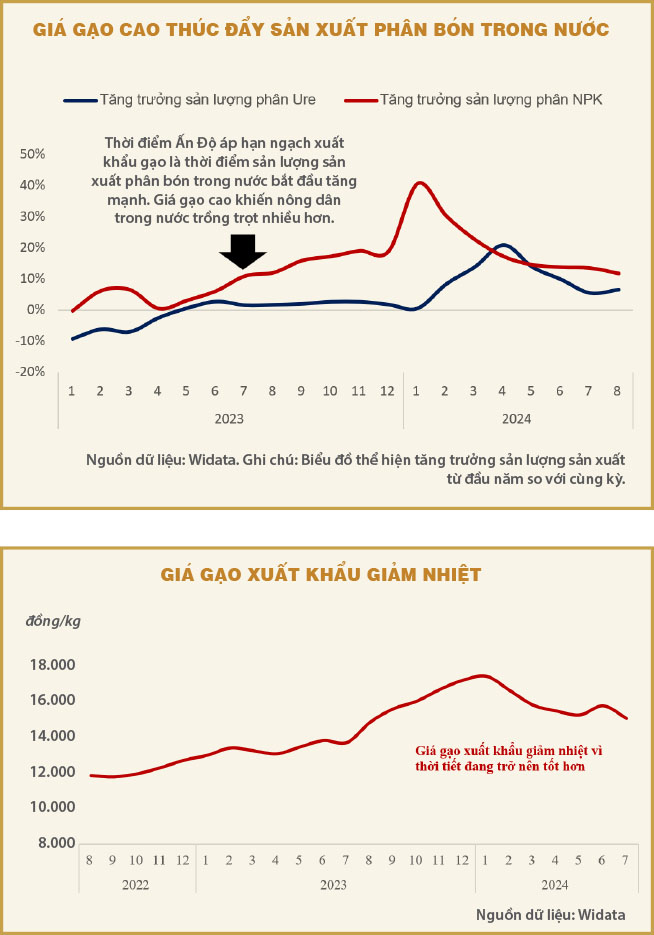
In addition, India’s rice export quotas also play an important role in creating growth for Vietnam’s fertilizer industry. India, affected by the El Nino phenomenon, had to reduce domestic rice production, forcing them to impose export quotas to ensure domestic food security. This pushed up global rice prices, creating favorable conditions for Vietnamese rice exporters. As a result, domestic demand for fertilizers increased sharply to serve rice production. This is a great advantage for businesses in the fertilizer industry, helping them maintain stable output and revenue in the context of global rice prices continuing to rise.
∗ El Nino is a term used to describe the abnormal warming of sea water in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean, which affects weather globally. El Nino is not a local phenomenon, but part of a large-scale, complex interacting system.
Stable profit margin
The stability of oil prices also plays an important role in keeping the cost of fertilizer production at a reasonable level. Oil prices are a major cost in the fertilizer production process and the lack of fluctuations in oil prices has helped the fertilizer industry to be more stable in terms of costs. This creates favorable conditions for businesses in the industry to optimize production processes and keep profit margins stable.
In the second quarter of 2024, the industry’s gross profit margin reached 11.7%, a slight increase from 11.2% in the first quarter, showing a sustainable growth trend. However, it is worth noting that the after-tax profit margin decreased from 3.9% in the first quarter to 3.1% in the second quarter, reflecting the increase in operating expenses and other factors affecting after-tax profit.
Oil prices are a major cost factor in the fertilizer production process, and the lack of fluctuations in oil prices has helped the fertilizer industry to be more stable in terms of costs. The lack of fluctuations in oil prices is an important factor that helps businesses in the industry to control production costs well. As a result, businesses can take advantage of opportunities to manage costs effectively, thereby maintaining reasonable profit margins. This also helps the fertilizer industry to increase its competitiveness in the international market, especially when the demand for fertilizers remains high.
World economic and political situation
- Impact of War in the Middle East: The war situation in the Middle East affects the nitrogen fertilizer market in 2024. About 51% of global urea exports originate from the Middle East, and Israel is the fourth largest producer of potash in the world.
- China restricts urea exports: China restricts urea exports to ensure stable domestic supply. To protect domestic supply, Russia also extended its policy of applying fertilizer export quotas.
- Egyptian government cuts gas supplies indefinitely: The Egyptian government has decided to indefinitely extend gas supply cuts.
- EU urea production expected to remain low: Urea production in the EU is expected to remain low as the cost of urea production in the region remains much higher than the cost of importing urea from Egypt.
→ All of the above factors affect the world fertilizer supply and increase fertilizer prices.
FERTILIZER MARKET IS GRADUALLY COOLING DOWN IN THE LAST MONTHS OF THE YEAR AFTER A PERIOD OF STRONG DEVELOPMENT
The fertilizer market began to cool down in the last months of 2024, when the global weather situation gradually became more stable. The El Nino phenomenon is gradually disappearing according to ONI index data, September 28, 2024 The Indian government has suspended the rice export ban on non-basmati milled rice, ending a ban that lasted more than 14 months, which has directly affected Vietnam’s rice export prices and led to a decline in fertilizer demand.
In fact, fertilizer production in June showed signs of decline as global rice prices began to decline slightly. This shows that the growth of the fertilizer industry not only depends on domestic demand but is also greatly influenced by fluctuations in the international market. According to a report by the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development, the domestic fertilizer market is in a saturated state with supply exceeding demand in the Urea/Phosphate and NPK segments.
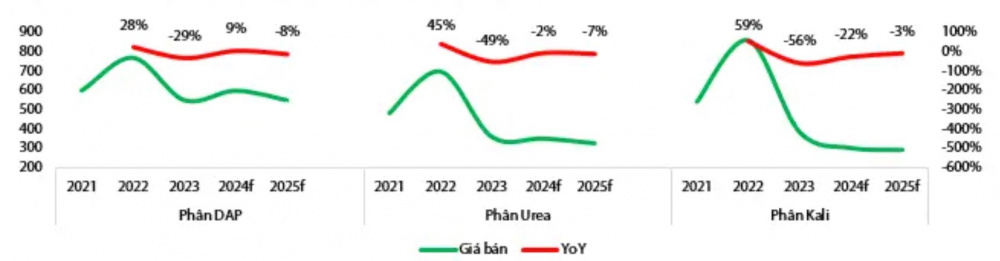
Under pressure from oversupply, fertilizer prices on the world market are expected to gradually decrease in the period 2024 – 2025. (Source: World Bank, Rong Viet Securities)
Therefore, Vietnamese enterprises have been looking for ways to boost exports to countries where world demand is high. However, gaining market share from urea exporting powers is still difficult as Vietnam’s production costs are much higher than those of major producing countries such as Russia, Egypt, and China, according to Rong Viet Securities.
ONI is an anomaly in the average temperature of 3 consecutive months that deviates from the average temperature in the surface waters of the eastern-central tropical Pacific Ocean.
An index value of +0.5 or greater indicates El Nino.

 vn
vn
















